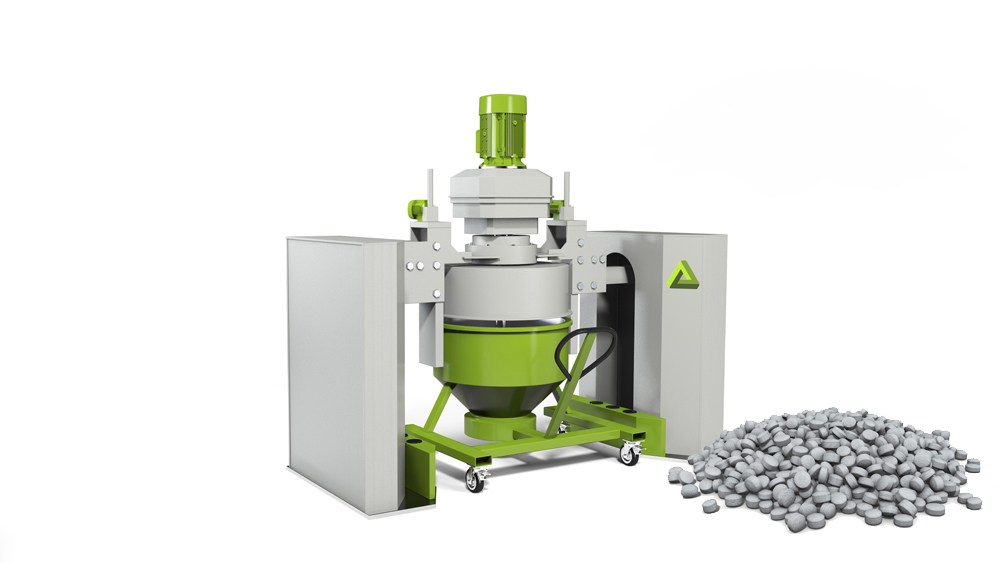
Feedstock
Feedstock
Feedstock (initial material) consists of fine metal powders, which are mixed with thermoplastics and additives in special mixing machines. The compounding process is completed when metal particles in the binder are fully homogenized. After completion of the process, the material is granulated into pellets.
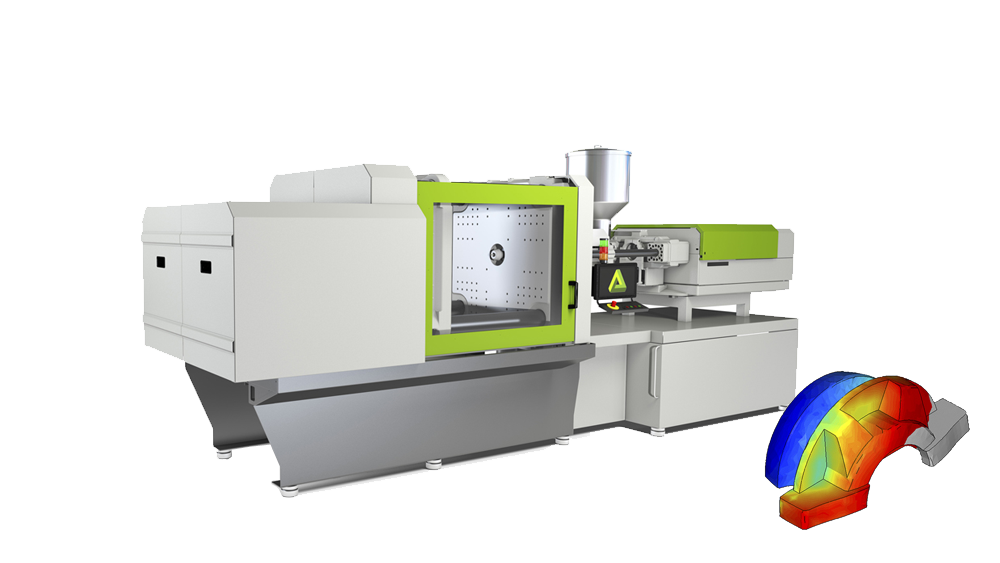 Injection molding
Injection molding
In this process step, the feedstock is injected into a mold under high pressure using conventional injection molding machines. In this way, MIM combines the advantages of the design freedom of plastic injection molding with the excellent mechanical and thermal resilience of metallic materials.
The result of the injection molding process is the so-called “green part”, which is up to 20% larger than the sintered final component, depending on the feedstock used.
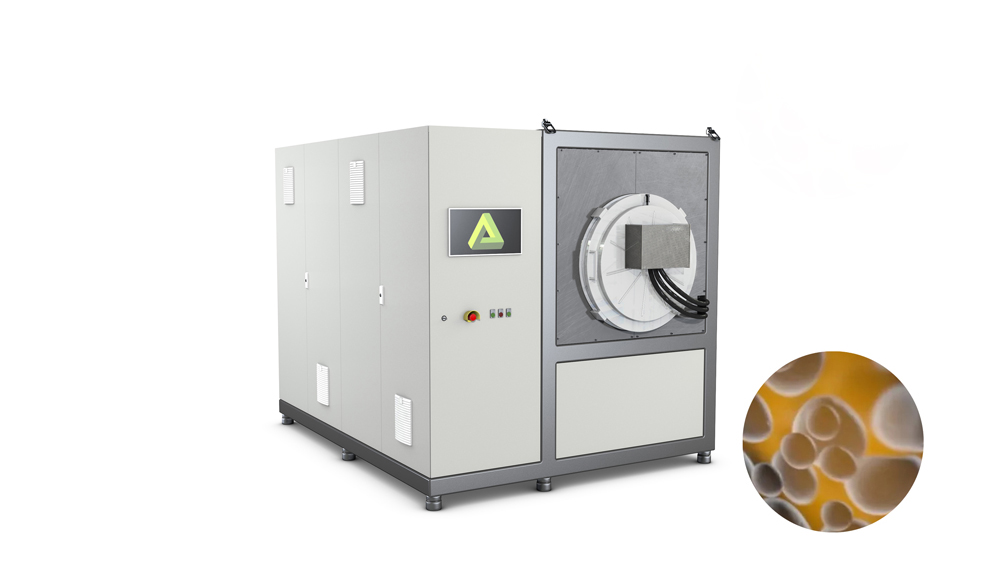 Debinding
Debinding
Debinding can be catalytic, thermal or solvent-based depending on the binder system. The binder is removed from the component with the exception of a residual binder content of 2-3t% (backbone). The residual binder guarantees the stability of the so-called “brown part” for the subsequent process.
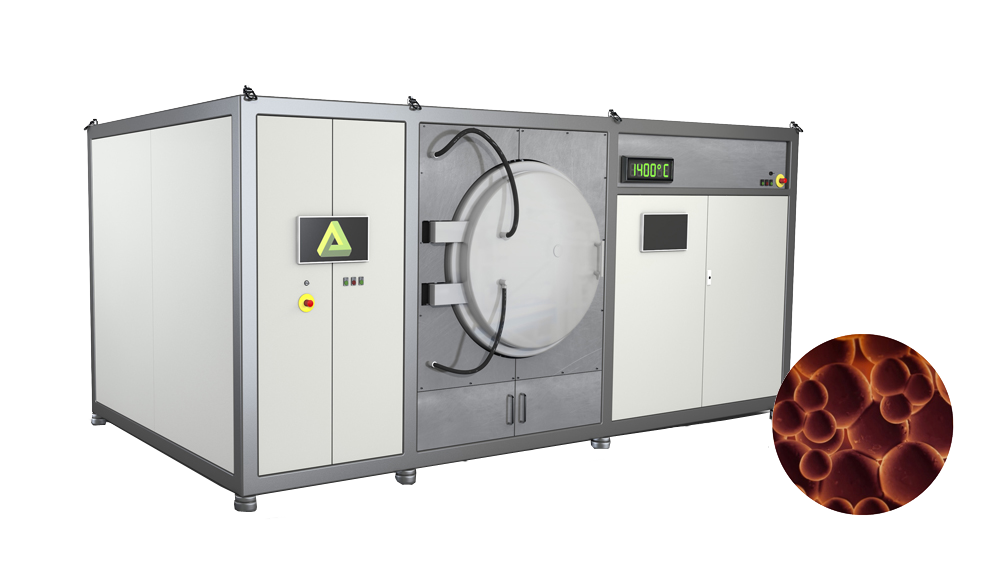 Sintering
Sintering
In the final step, the components are sintered at temperatures between 1200°C and 1400°C depending on the material. At this step, the remaining binder is completely removed. When sintering, the parts shrink isotopically to the desired dimensions. Sintered parts are completely metallic and have densities of >97%. As a result, they have properties similar to those of the machined components.
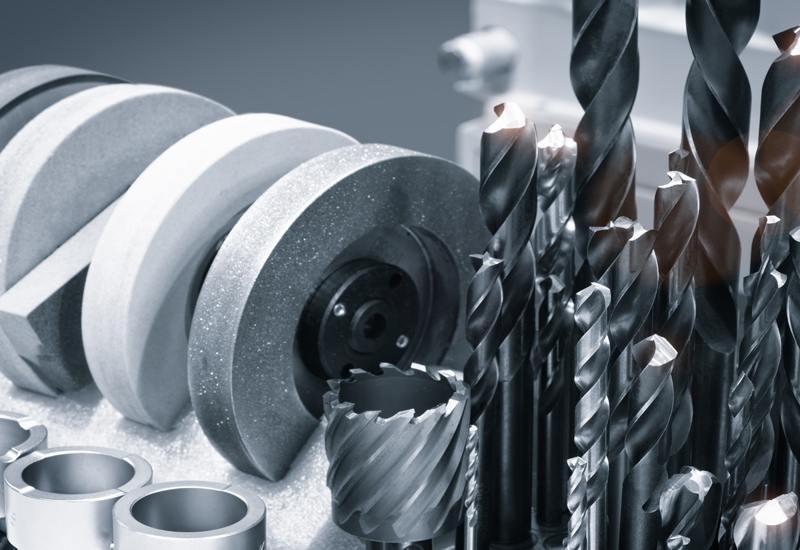 Post-processing
Post-processing
MIM parts, as any metal parts, can be heat-treated and further processed, for example, to achieve better tolerances at critical dimensions. MIMplus Technologies offers a wide range of post-processing technologies such as hardening, CNC machining, laser machining, surface technologies and joining techniques including the assembly of complete subassemblies.